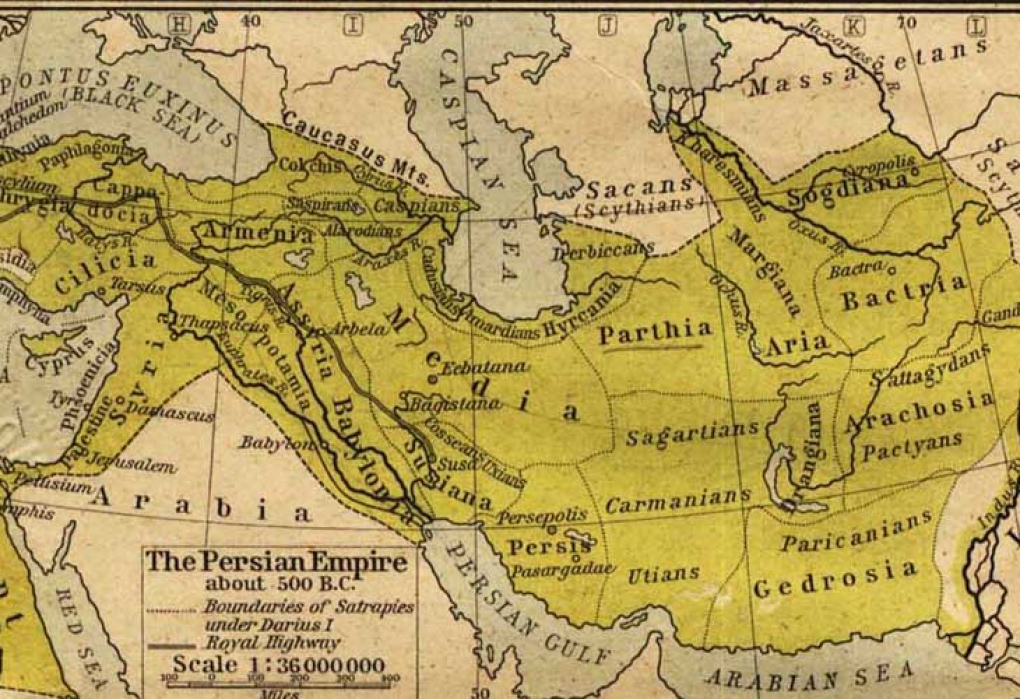
Archaeology shows that pistachio seeds were a common food as early as 6750 BC. Pliny the Elder writes in his Natural History that pistacia, "well known among us", was one of the trees unique to Syria, and that the seed was introduced into Italy by the Roman Proconsul in Syria, Lucius Vitellius the Elder (in office in 35 AD) and into Hispania at the same time by Flaccus Pompeius.The early sixth-century manuscript De observatione ciborum ("On the observance of foods") by Anthimus implies that pistacia remained well known in Europe in Late Antiquity. Archaeologists have found evidence from excavations at Jarmo in northeastern Iraq for the consumption of Atlantic pistachio. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were said to have contained pistachio trees during the reign of King Merodach-Baladan about 700 BC